Irradiance Cache (Legacy)
辐照度缓存(遗产)
Tip: 提示:Note also that the old Irradiance Cache does not work with Team Render. Using the old Irradiance Cache with Team Render will result in Cinema 4D automatically switching to the new Irradiance Cache (with correspondingly different results).
还要注意,旧的辐照度缓存不能与团队渲染一起使用。使用旧的辐射缓存与团队渲染将导致C4D 自动切换到新的辐射缓存(与相应不同的结果)。
 Left rendered using the Irradiance Cache method
(medium), right rendered using the 使用辐照度缓存方法(介质)左渲染,使用QMC method. For each,
Diffuse Depth value was set to 3. Render time for the Irradiance Cache method was a fraction of the time
required for the QMC method. 方法。对于每一个,漫射深度值被设置为3。辐照度缓存方法的渲染时间只是 QMC 方法所需时间的一小部分
Left rendered using the Irradiance Cache method
(medium), right rendered using the 使用辐照度缓存方法(介质)左渲染,使用QMC method. For each,
Diffuse Depth value was set to 3. Render time for the Irradiance Cache method was a fraction of the time
required for the QMC method. 方法。对于每一个,漫射深度值被设置为3。辐照度缓存方法的渲染时间只是 QMC 方法所需时间的一小部分
The advantages of the Irradiance Cache method (hereinafter referred to as "IR") of rendering GI are moderate render times combined with a very homogeneous and even dispersion of light. artefacting (e.g., spots) that was common in previous versions of GI no longer occur when common settings are used. Also, flickering areas within an animation are also a thing of the past.
辐射缓存方法(以下简称“ IR”)渲染 GI 的优点是适中的渲染时间和非常均匀甚至分散的光线。在使用公共设置时,以前版本的 GI 中常见的遗留物(如斑点)不再出现。此外,动画中闪烁的区域也是过去的事情。
The IR calculation analyses the scene by making several pre-calculations ("pre-passes") in order to determine the most pertinent areas of the scene ("shading points" - the points shown in the pre-passes) so it can ascertain the correct indirect illumination. The brightness values of these shading points will then be saved to the Irradiance Cache as a "Record". This cache can be saved and later reused.
红外计算通过对场景进行多次预计算(“预通道”)来分析场景,以确定场景中最相关的区域(“阴影点”——预通道中显示的点) ,从而确定正确的间接照明。这些明暗点的亮度值将被保存到辐照度缓存中作为“记录”。这个缓存可以保存并在以后重用。
The Irradiance Cache Records will be interpolated for the final rendering in order to "supply" indirect light to the pixels between the shading points.
辐射缓存记录将被插入最终渲染,以便“提供”间接光的像素之间的阴影点。
There are, however, certain disadvantages to using the Irradiance Cache method:
然而,使用 Irradiance Cache 方法有一些缺点:
Finer details pertaining to light and shadow can be omitted due to the interpolation between a limited number of shading points. This is where the QMC method has an edge. This is why the IR method offers a Details Enhancement option that combines QMC and IR methods in order to compensate for this disadvantage. The IR method offers numerous additional parameters that let you push its rendering capabilities to the limit for every scene.
由于在有限数量的阴影点之间进行插值,有关光和阴影的细节可以省略。这就是 QMC 方法的优势所在。这就是为什么 IR 方法提供了一个结合 QMC 和 IR 方法的 Details Enhancement 选项,以弥补这个缺点。IR 方法提供了许多额外的参数,这些参数可以让你将它的渲染能力推到每个场景的极限。
Number of Samples Calculated Per Shading Point
每个遮光点计算的样本数
 A certain number of samples are beamed into the
scene from each shading point. 一定数量的样本从每个阴影点传送到场景中
A certain number of samples are beamed into the
scene from each shading point. 一定数量的样本从每个阴影点传送到场景中
In the General tab you can define the number of samples in the Project in order to ascertain the brightness and color ("sample"), interpolate these values and save them to the cache as "Records".
在“常规”选项卡中,您可以定义项目中的样本数量,以确定亮度和颜色(“样本”) ,插值这些值,并将它们保存到缓存中作为“记录”。
The more samples that are calculated, the more precise the GI calculation will be for that shading point.
越多的样本,计算,更精确的 GI 计算将为阴影点。
 Increasing number of samples from left to right.
All other settings remain the same. 从左到右增加样本数量。所有其他设置保持不变
Increasing number of samples from left to right.
All other settings remain the same. 从左到右增加样本数量。所有其他设置保持不变
As you can see in the image above, sample values that are too low result in a grainy rendering, especially in the corners. If you look closely you will see several spots just over the baseboard at the right of the scene. These can be removed using one of these methods:
正如你在上面的图像中看到的,样本值太低会导致呈现出颗粒状,特别是在角落。如果你仔细观察,你会发现在场景右侧的踢脚板上方有几个斑点。这些问题可以通过以下方法之一来解决:
阴影点的散布

Increasing shading point densities from left to right. In the example above, the difference is most noticeable in the room corners and shelf shadows. Note also how the shadow density increases from left to right.
从左到右增加遮光点密度。在上面的例子中,房间角落和架子阴影的区别最为明显。还要注意阴影密度是如何从左到右增加的。
The next six parameters are used to define the dispersion of density of the shadow points between which brightness and color are interpolated during rendering. Increased density results in more recognizable details such as shadows (which is, however, also dependent on the Smoothing settings, which can, in turn, cause details to become less visible if set too high).
接下来的六个参数用于定义阴影点的密度分布,在渲染过程中,亮度和颜色在阴影点之间被插值。增加密度会产生更多可识别的细节,比如阴影(不过,这也取决于平滑设置,如果设置得太高,这反过来会导致细节变得不那么可见)。
As you can see in the example above, smooth surfaces with no edges, corners or similar features receive comparatively few shading points whereas "complex" areas in which a lot of shading and lighting take place contain many shading points. This differing dispersion takes place automatically when the default settings are used and is a result of the fact that indirect illumination in corners and at edges changes greatly.
正如你在上面的例子中看到的,没有边、角或类似特征的光滑表面得到的阴影点相对较少,而大量阴影和照明发生的“复杂”区域包含许多阴影点。当使用默认设置时,这种不同的色散会自动产生,这是角落和边缘的间接照明发生很大变化的结果。
Tip: 提示:记录密度
This parameter contains a set of predefined parameters that are by default optimized for most uses. Only under special circumstances should you change the option to Custom and modify these parameters yourself.
此参数包含一组预定义参数,默认情况下,这些参数针对大多数用途进行了优化。只有在特殊情况下,您才应该将选项更改为 Custom 并自己修改这些参数。
习俗
This option will automatically be selected if one of the underlying parameters is modified.
如果修改了其中一个基础参数,将自动选择此选项。
预览
As the name suggests, a preview will be rendered quickly - with correspondingly "poor" values that make a quick rendering possible. These "poor" values will result in many GI details being lost or in faulty rendering. This option is especially useful for creating animation preview renderings.
顾名思义,预览将快速呈现——相应的“穷”值使快速呈现成为可能。这些“差”值将导致许多 GI 细节丢失或在错误的渲染。这个选项对于创建动画预览渲染特别有用。
Low
Medium
High
High (Details)
低中高中(详情)
These four options are optimized for use with the Least Squares interpolation method and result in differing levels of quality.
这四个选项都经过优化,以便与最小二乘插值法一起使用,从而达到不同的质量水平。
Min Rate[-8..4]
Max Rate[-8..4]
最低利率[-8. . 4]最高利率[-8. . 4]
When Cinema 4D creates an Irradiance Cache it initially starts with a lower image resolution (Min. Rate) and progresses pre-pass-by-pre-pass to the final IR resolution (Max. Rate). A value of 0 results in full resolution (pixel size 1*1), a value of -1 = pixel size of "2*2", -2 = "4*4" and so on. The Min Rate value should logically be smaller than the Max Rate value. Positive values can also be applied, which will allow cache Records in the sub-pixel range (can be useful for Sub-polygon Displacement if details are lost).
当Cinema 4D 创建一个辐射缓存它最初以较低的图像分辨率(最小。速率)和进展通过前预通过到最终的红外线分辨率(最大。息率)。0的值得到完整的分辨率(像素大小1 * 1) ,-1 = 像素大小“2 * 2” ,-2 = “4 * 4”等等。最小速率值逻辑上应小于最大速率值。正值也可以应用,这将允许缓存记录在亚像素范围(可用于亚多边形位移,如果细节丢失)。
These resolutions apply only to IR calculations. Since the Irradiance Cache can be scaled relatively easily (i.e. lower IR resolution at larger image resolution) good results can often be achieved even when using smaller resolutions. Hence, these two parameters offer great potential for shortening render times, especially for brightly illuminated, low-detail scenes.
这些分辨率仅适用于红外线计算。由于辐照度缓存可以相对容易地缩放(即较低的红外线分辨率较大的图像分辨率) ,即使使用较小的分辨率,也常常可以取得很好的效果。因此,这两个参数为缩短渲染时间提供了巨大的潜力,特别是对于明亮的、低细节的场景。
Here’s the proof:
以下就是证据:
 As you can see in the images above, the render time
is practically cut in half. Although GI artefacting increases, this is usually barely recognizable in brightly
lit scenes. 正如你在上面的图片中看到的,渲染时间实际上减少了一半。虽然 GI 的人工制品增加,这通常是难以辨认在明亮的场景
As you can see in the images above, the render time
is practically cut in half. Although GI artefacting increases, this is usually barely recognizable in brightly
lit scenes. 正如你在上面的图片中看到的,渲染时间实际上减少了一半。虽然 GI 的人工制品增加,这通常是难以辨认在明亮的场景
For example, a setting of -3/0 renders faster than a setting of 0/0 with practically the same result. Equal values (e.g., -3/-3) result in only a single pass at the defined resolution.
例如,-3/0的设置比0/0的设置速度快,几乎得到相同的结果。相等的值(例如-3/-3)只在定义的分辨率上通过一次。
半径[0. . 100% ]
 A variation of the 一个变异的Radius 半径, Minimum Radius 最小半径 and 及Density
Control 密度控制 parameters. The 参数Use Proximity Correction 使用邻近修正 was disabled (creates
additional shading points). In our example the shading points have been colored red for better
visibility. 被禁用(创建额外的阴影点)。在我们的例子中,为了更好的能见度,阴影点被涂成了红色
A variation of the 一个变异的Radius 半径, Minimum Radius 最小半径 and 及Density
Control 密度控制 parameters. The 参数Use Proximity Correction 使用邻近修正 was disabled (creates
additional shading points). In our example the shading points have been colored red for better
visibility. 被禁用(创建额外的阴影点)。在我们的例子中,为了更好的能见度,阴影点被涂成了红色
This parameter defines the maximum distance between shading points. The lower the value the more densely the points will lie together. This parameter primarily affects non-critical regions of the scene such as flat, clear surfaces. The effect of this parameter is also dependent on the Density Control value.
此参数定义着色点之间的最大距离。值越低,这些点就越密集地聚集在一起。这个参数主要影响场景中的非关键区域,如平坦、清晰的表面。这个参数的影响也取决于密度控制值。
最小半径[0. . 100% ]
This parameter defines the minimum distance between shading points. It primarily affects the critical regions of the scene such as corners, edges, etc. The lower the value the more densely the shading points will lie at these regions. This parameter works proportional to the Radius parameter, i.e., if this value is halved the Minimum Radius value will be halved internally as well.
此参数定义着色点之间的最小距离。它主要影响场景的关键区域,如角落、边缘等。值越低,阴影点位于这些区域的密度就越大。这个参数与半径参数成正比,也就是说,如果这个值减半,内部的最小半径值也会减半。
The Minimum Radius parameter primarily affects areas in which details are important (e.g., subtle shadows). However, too many shading points in these areas can cause problems.
最小半径参数主要影响细节非常重要的区域(例如,细微的阴影)。然而,在这些地区过多的阴影点可能会导致问题。
In order to make subtle details visible, use the Details Enhancement parameters instead.
为了使细微的细节可见,改为使用 Details Enhancement 参数。
密度控制[0. . 100% ]
In contrast to the previous two parameters that primarily affect critical or non-critical regions, this parameter affects the shading points globally throughout the scene. The higher the value the greater the density.
与前两个主要影响关键区域或非关键区域的参数相反,这个参数影响整个场景的阴影点。值越高,密度越大。
使用邻近修正
This is one of the many GI pre-passes and is responsible for having neighboring shading points "assist" each other in critical regions and pass on information regarding the proximity of geometry. New shading points are created and calculated during this process.
这是许多 GI 预传递之一,并负责有邻近的阴影点“协助”在关键区域的其他方面,并传递信息的接近几何。在此过程中将创建和计算新的阴影点。
This behavior can be disabled here, which will save some render time but also result in poorer render quality (especially in corner and on edges).This option should be disabled if you are using a Max. Rate value of less than 0. Otherwise unnecessary calculations will result.
这个行为可以在这里禁用,这将节省一些渲染时间,但也会导致较差的渲染质量(特别是在角落和边缘)。如果您正在使用 Max,则应禁用此选项。率值小于0。否则将导致不必要的计算。
Irradiance Cache Interpolation
辐照度缓存插值
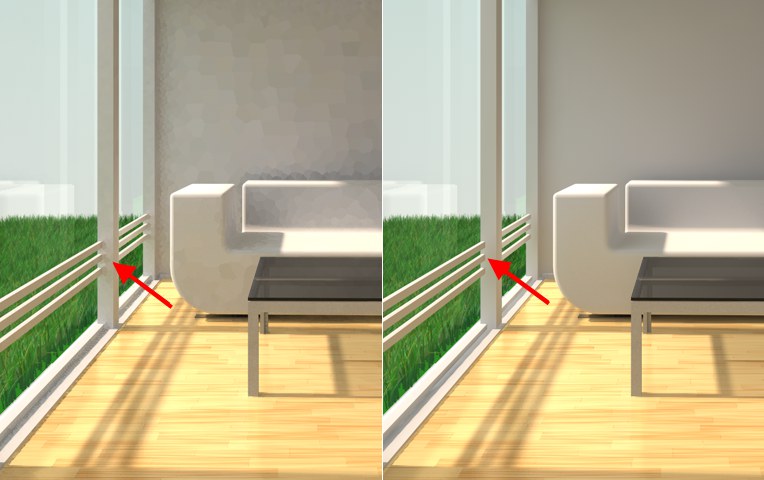 Left before and right after smoothing. Note how
smoothing eliminates subtle details like the shadows of the window bars. 左前右后平滑。注意平滑如何消除细微的细节,如窗口条的阴影
Left before and right after smoothing. Note how
smoothing eliminates subtle details like the shadows of the window bars. 左前右后平滑。注意平滑如何消除细微的细节,如窗口条的阴影
All previously described parameters dealt with the placement of shading points and their calculation. The indirect illumination was ascertained for the most critical areas of the scene. In the end the point-by-point dispersion of luminosity must be turned into an Area dispersion for rendering. This is what smoothing does by default: For each surface pixel to be rendered, the Irradiance Cache will be examined to find the Record of the pixel in its immediate proximity in order to interpolate the brightness and color values for that pixel. How this interpolation is done (how many Records and in which proximity should be taken into account?) is determined using the parameters described below:
所有以前描述的参数涉及到阴影点的位置及其计算。对场景中最关键的区域确定了间接照明。最后,光度的逐点色散必须转化为面积色散来渲染。默认情况下平滑是这样做的: 对于每个要渲染的表面像素,辐照度缓存将被检查以找到其直接接近的像素记录,以插值该像素的亮度和颜色值。这种插值是如何进行的(应该考虑多少条记录以及哪些邻近性?) 使用下述参数来确定:
Tip: 提示:This can be compensated for using the following methods:
这可以通过以下方法得到补偿:
插值方法
最小二乘法
As is so often the case, this term has its origins in mathematics. What this function essentially does is calculate a curve based on a limited number of points. And this is basically all that happens for smoothing: The Irradiance Cache contains a limited number of Records from which a homogeneous, even dispersion of illumination should be calculated for the entire image.
通常情况下,这个术语起源于数学。这个函数实际上是基于有限数量的点计算一条曲线。这基本上就是平滑所发生的一切: 辐照度缓存包含有限数量的记录,从这些记录中可以计算出整个图像的均匀甚至散射光。
加权平均数
This method of interpolation works similarly to the Least Squares method, only that it only interpolates between values (whereas the Least Squares method can also extrapolate, i.e.brighter or darker results than represented by the values defined). So, what is this good for? This method can prevent artefacting when using low-quality GI settings. Furthermore, this method will render faster than the Least Squares method. Disadvantage: The dispersion of light is less homogenous than when using the Least Squares method.
这种插值方法的工作原理与最小二乘法类似,只是它只在值之间插值(而最小二乘法也可以外推,即比定义的值所表示的结果更亮或更暗)。那么,这有什么好处?此方法可以防止在使用低质量的 GI 设置时产生伪制品。此外,这种方法将渲染速度比最小二乘法。缺点: 光的色散不如使用最小二乘法时均匀。
没有
If this option is selected, no smoothing will take place.
如果选择此选项,则不会进行平滑处理。
平滑
A higher degree of smoothing results more details that will be lost but also in a more homogeneous dispersion of light. Select Custom to manually define the Records and Scale values.
更高程度的平滑会导致更多的细节丢失,但也会导致更均匀的光散射。选择 Custom 手动定义 Records 和 Scale 值。
记录[8.256]

The Scale and Records values limit the number of shading points to be used (the shading points above have been colored red for display purposes).
Scale 和 Records 值限制了要使用的阴影点的数量(为了显示目的,上面的阴影点已经被涂成红色)。
The Records parameter defines per pixel to be rendered the maximum number of surrounding Records in the Irradiance Cache that should be included in the interpolation of color and brightness for that pixel. If, however, the Scale value is so low that not enough Records can be included in the interpolation, it may result that fewer Records are included.
Records 参数定义每个像素要渲染的辐照度缓存中周围记录的最大数量,这些记录应该包含在该像素的颜色和亮度插值中。但是,如果 Scale 值太低,以至于插值中不能包含足够的 Records,则可能会导致包含的 Records 更少。
The lower the parameter value the fewer Records that will be included in the final interpolation and the less homogeneous the rendering will turn out. Higher values will result in more smoothing but also take correspondingly longer to render.
参数值越低,最终插值中包含的记录就越少,呈现结果的同构性也就越低。更高的值将导致更平滑,但也相应地需要更长的渲染时间。
比例[1.6. . 8]
This parameter serves to spatially limit the Records included in the interpolation process. The larger the value the more Records that will be included and the softer the interpolation will be - and the longer it will take to render. Alternatively the Records parameter can be used for this purpose.
此参数用于在空间上限制插值过程中包含的记录。越大的值,将包括更多的记录和软插值将-和更长的时间将需要渲染。或者,可以为此目的使用 Records 参数。
辐照度缓存优化
缓存精化
 The 这个Cache Refinement 缓存精化
parameter creates additional shading points in areas with high contrast. Each image contains an insert with
the final rendering. 参数在高对比度的区域创建额外的阴影点。每个图像都包含一个带有最终呈现的插入
The 这个Cache Refinement 缓存精化
parameter creates additional shading points in areas with high contrast. Each image contains an insert with
the final rendering. 参数在高对比度的区域创建额外的阴影点。每个图像都包含一个带有最终呈现的插入
The previously described parameters all dealt with the placement of shading points based on a scene’s geometric properties. But what if a coarse, dark GI shadow disturbs the entire image?
前面描述的参数都是基于场景的几何特性来处理阴影点的位置。但是,如果粗糙,黑暗的胃肠阴影干扰整个图像?
This is where the Cache Refinement parameter comes in: It compares the Records in the Irradiance Cache and generates additional Records (i.e. shading points) in areas with high contrast (brightness and color) in order to refine and render these areas more precisely.
这就是 Cache refining 参数的作用所在: 它比较 Irradiance Cache 中的记录,并在高对比度(亮度和颜色)的区域生成额外的记录(即阴影点) ,以便更精确地细化和渲染这些区域。
Tip: 提示:Higher Cache Refinement settings will lead to longer render times but no necessarily to better render quality.
更高的缓存细化设置将导致更长的渲染时间,但不一定更好的渲染质量。
通过[0. . 4]
Color correction can also take up several passes (Multi-Passes). Each new pass includes the results of the previous pass and refines it further by creating additional shading points in critical areas.
色彩校正也可以进行多次通行(Multi-Passes)。每个新的通行证包括结果,以前的通行证和细化它进一步创造额外的阴影点在关键领域。
Use this setting to define the frequency with the cache should be defined.
使用此设置定义应该定义的缓存频率。
颜色阈值[0. . 100% ]
 Top: Prior to cache refinement. Bottom: After cache
refinement. Left smaller, right larger 高速缓存精化之前。底部: 在缓存精化之后。左边小,右边大Color Threshold 色彩阈值 value. 价值
Top: Prior to cache refinement. Bottom: After cache
refinement. Left smaller, right larger 高速缓存精化之前。底部: 在缓存精化之后。左边小,右边大Color Threshold 色彩阈值 value. 价值
This value defines the degree to which (neighboring) cache Records can deviate from each other with regard to their color (intensity) before additional shading points ("Samples") are added. The lower the value the lower the deviation threshold will be and the more samples that will be added.
这个值定义了在添加额外的阴影点(“示例”)之前,(邻近的)缓存记录在颜色(强度)方面相互偏离的程度。值越低,偏差阈值越低,将添加更多的样本。
Tip: 提示:截止[0. . 100% ]
This values additionally includes differences in intensity. The lower the value the greater the differences between Records have to be for the color correction to apply. A value of 0 will turn cache refinement off.
这个值还包括了强度的差异。值越低,记录之间的差异就越大,这样色彩校正就可以应用。值0将关闭缓存细分。
力量[0. . 200% ]
This parameter is used to adjust the cache refinement’s overall sample density. A value of 0 will turn cache refinement off whereas larger values will increase the number of shading points ("Samples") correspondingly while taking into account Color Threshold and Cutoff values.
该参数用于调整缓存精化的总体采样密度。值0将关闭缓存细化,而较大的值将相应地增加阴影点(“样本”)的数量,同时考虑到颜色阈值和截止值。
距离图
 The 这个Distance Map 距离图
prevents light from passing through surfaces. 防止光线穿过表面
The 这个Distance Map 距离图
prevents light from passing through surfaces. 防止光线穿过表面
Enabling this option generates additional information regarding proximal geometry (any edges nearby?) for each Record in the Irradiance Cache. When values from the Irradiance Cache are used for interpolation when the image is rendered, the Distance Map will be included in the calculations, i.e., interpolation will not occur "around a corner" or through (a thin) wall, which results in artefacting ("light leaks").
启用此选项将生成关于近端几何的附加信息(附近的任何边?)对于辐照度缓存中的每个记录。当使用辐照度缓存中的值进行图像渲染时的插值时,距离图将包含在计算中,即插值不会发生在“拐角处”或通过(薄)壁,从而导致加工(”光泄漏”)。
Of course the calculation of the Distance Map requires extra render time and this is why this option can be disabled if desired.
当然,距离贴图的计算需要额外的渲染时间,这就是为什么如果需要可以禁用这个选项的原因。
Another method of eliminating such artefacting is:
另一种消除这种人工制品的方法是:
检查记录可见性
 The 这个Check Record
Visibility 检查记录可见性 option prevents artefacting on the narrow frame. 选择防止人工制品在狭窄的框架上
The 这个Check Record
Visibility 检查记录可见性 option prevents artefacting on the narrow frame. 选择防止人工制品在狭窄的框架上
Activating this option will cause cache Records that are not included in the current angle of view of the camera to be disabled for rendering. So, what is this good for? As was the case with the previous parameter, this option also tries to eliminate "light leaks" (render artefacting). This parameter, however, primarily tries to eliminate "light leaks" through thin walls (e.g., single-polygon surfaces) as in our example above. Render time will increase slightly, hence this option should be used after noticing that artefacting actually occurs. This option can even be activated after an Irradiance Cache file has been saved.
激活此选项将导致在呈现时禁用未包含在相机当前视角中的缓存记录。那么,这有什么好处?与前一个参数的情况一样,这个选项也试图消除“光泄漏”(呈现人工制品)。然而,这个参数主要试图消除薄壁(例如,单边形表面)中的“光泄漏” ,如上面的例子所示。渲染时间将会稍微增加,因此这个选项应该在注意到工艺品实际发生后使用。此选项甚至可以激活后,辐照度缓存文件已保存。
细节增强
 Left with, right without enhanced details. Notice
the effect this parameter has on the small geometric details. 左边有,右边没有增强的细节。注意这个参数对小的几何细节的影响
Left with, right without enhanced details. Notice
the effect this parameter has on the small geometric details. 左边有,右边没有增强的细节。注意这个参数对小的几何细节的影响
The Details Enhancement parameter contains special options to counteract a characteristic of the Irradiance Cache - the "blurring" (smoothing) of details such as subtle shadows. The enhancement of details uses the QMC Sampling method (see also here) in critical areas (for each (!) relevant pixel) like corners, edges, cavities, etc. The Details Enhancement functionality can be seen as a special type of Ambient Occlusion whereby indirect light is included.
细节增强参数包含特殊的选项,以抵消特点的辐射缓存-“模糊”(平滑)的细节,如微妙的阴影。详细信息的增强在关键区域使用 QMC 抽样方法(另见此处)(对于每个区域(!)相关像素) ,例如角落、边缘、空洞等。细节增强功能可以看作是一种特殊类型的环境遮挡,即间接光是包括在内。
In a nutshell: Subtle geometry details are accentuated.
简而言之: 微妙的几何细节得到了强调。
Note that the internal Irradiance Cache will be calculated differently (the algorithm will be aware of the subsequent detail enhancements and will calculate the critical areas differently) if this option is disabled. However you do it, the Details Enhancement will be calculated separately for each rendered image, i.e., re-using a saved cache will reduce render times.
请注意,如果禁用此选项,内部辐照度缓存将以不同的方式计算(算法将知道随后的细节增强,并将以不同的方式计算关键区域)。不管你怎么做,细节增强都会针对每个渲染图像分别计算,也就是说,重用保存的缓存会减少渲染时间。
If you apply Details Enhancement you can lower the other Irradiance Cache settings (especially those pertaining to Record Density).
如果你应用细节增强,你可以降低其他辐射缓存设置(特别是那些属于记录密度)。
细节增强
Enables or disables the Details Enhancement parameter.
启用或禁用 Details Enhancement 参数。
自适应模式
Enabling this option can be an advantage in some circumstances, e.g., several small areas are more grainy than others. Additional samples will then be rendered in these areas.
启用此选项在某些情况下可能是一种优势,例如,一些小区域比其他区域更加粗糙。然后将在这些地区提供额外的样品。
中学预算
 Center, 中心、,Estimate
Secondary 中学预算 disabled, right enabled. A QMC rendering at the left for comparison. Note how the object
contact areas were darkened in the image on the right. 禁用,右启用。左边是一个 QMC 渲染图,用于比较。注意物体接触区域是如何在右边的图像中变暗的
Center, 中心、,Estimate
Secondary 中学预算 disabled, right enabled. A QMC rendering at the left for comparison. Note how the object
contact areas were darkened in the image on the right. 禁用,右启用。左边是一个 QMC 渲染图,用于比较。注意物体接触区域是如何在右边的图像中变暗的
This mode renders faster and offers good results for most applications. However, certain areas will be rendered too dark or too colorful as opposed to a pure QMC rendering (GI ModeQMC), which generally doesn’t matter the least bit in most cases. If desired, this behavior can also be disabled (note that grainy renderings can result, in which case the Quality Ratio value should be raised).
这种模式呈现更快,并为大多数应用程序提供良好的结果。然而,与纯 QMC 渲染(GI ModeQMC)相比,某些区域渲染得太暗或太多彩,在大多数情况下,这一点都不重要。如果需要,这种行为也可以禁用(注意,颗粒状渲染可能会导致,在这种情况下,质量比值应该提高)。
半径[0.05. . 0.25]
 Left: Small 左图: SmallRadius 半径
value. Right: Larger 价值。右: 更大Radius 半径 value. 价值
Left: Small 左图: SmallRadius 半径
value. Right: Larger 价值。右: 更大Radius 半径 value. 价值
Use this setting to define the radius within which neighboring objects, corners and edges should be included. Lower values result in only elements in the immediate proximity being "seen", whereas larger values will "see" elements correspondingly far away. Larger values will also result in higher precision and therefore longer render times.
使用这个设置来定义相邻物体、角和边应该包括在内的半径。较低的值只会导致直接接近的元素被“看到” ,而较大的值将相应地“看到”较远的元素。更大的值也会导致更高的精度,因此更长的渲染时间。
品质比率[5. . 1000% ]
As mentioned at the start, QMC Sampling will take place in critical areas. The Quality Ratio defines how many samples should be used per pixel, which in turn simply defines the graininess of the Details Enhancement. Larger values result in less grainy, softer results but require correspondingly longer render times.
正如在开始提到的,QMC 抽样将在关键领域进行。质量比定义了每个像素应该使用多少样本,这反过来又简单地定义了细节增强的颗粒度。较大的数值会导致较小的颗粒,较软的结果,但相应地需要较长的渲染时间。
Quality Ratio is an autonomous value that works independently of the rest of the IR settings (a value of 100% is equivalent to 64 samples).
质量比是一个独立于其他红外设置(100% 的值相当于64个样本)的自治值。
模式

The options in this drop-down menu are for test purposes only so the effects of the detail enhancement, which are often very subtle, can be made more visible. You can select from the following options:
这个下拉菜单中的选项仅用于测试目的,因此细节增强的效果(通常非常微妙)可以变得更加可见。你可以从以下选项中选择:
结合(正常)
Renders accurate results.
呈现精确的结果。
仅供参考(预览)
Renders detail enhancement without GI. Makes the detail enhancment most visible of all options.
在没有 GI 的情况下呈现细节增强。使细节增强在所有选项中最为可见。
全球唯一(预览)
Renders indirect illumination only.
只渲染间接照明。