 Cloth Tag 布标签Basic 基础Tag 标签Forces 力量Dresser 梳妆台Cache 缓存Expert 专家
Cloth Tag 布标签Basic 基础Tag 标签Forces 力量Dresser 梳妆台Cache 缓存Expert 专家
Tag Properties
标签属性
The settings found on this tab affect the actual structure of the control cage. This also provides functions that handle the stored calculations of the cloth simulation.
在此选项卡上找到的设置会影响控制笼的实际结构。这也提供了处理布料模拟的存储计算的函数。
自动启动/停止
If the Auto option is enabled, the Cloth engine will be linked to the maximum length of the current scene. In the Project Settings dialog, for example, if the Maximum frame is set to 150, the cloth engine will calculate for the entire 150 frames.
如果启用自动选项,布料引擎将链接到当前场景的最大长度。在项目设置对话框,例如,如果最大帧设置为150,布引擎将计算整个150帧。
When the Auto checkbox is disabled, the Start and Stop field will become active. This allows for the length of time at which the cloth engine will calculate for.
当“自动”复选框被禁用时,“开始”和“停止”字段将处于活动状态。这考虑到了布料发动机计算的时间长度。
迭代[1.2147483647]
This parameter basically controls the overall elasticity of a fabric. In Cinema 4D versions prior to R11.5 this was automatically defined internally (primarily based on the object subdivision and Stiffness setting), which however presented several disadvantages. The new incarnation allows for a separate, manual definition. Note that render times will increase as the defined value is increased and values near 0 can lead to unstable cloth calculations, which can then virtually "explode".
这个参数基本上控制了织物的整体弹性。在 R11.5之前的 Cinema 4D 版本中,这是自动在内部定义的(主要基于对象的细分和刚度设置) ,但也存在一些缺点。新的化身允许一个单独的,手动定义。请注意,渲染时间将随着定义值的增加而增加,接近0的值会导致不稳定的布料计算,这可能会实际上“爆炸”。
Iterations should be viewed as a mass for the overall stiffness of a fabric, which can be adjusted using the Stiffness, Flexion and Rubber parameters.
迭代应该被看作是织物整体刚度的质量,可以通过刚度、屈曲和橡胶参数进行调整。
If an older scene is loaded (prior to R11.5) the Iterations and Stiffness parameters will be set so the original Cloth behavior is maintained.
如果加载了一个旧的场景(在 R11.5之前) ,迭代和刚度参数将被设置,以保持原始的布料行为。
僵硬度[0. . 100% ]
This parameter controls the overall stiffness of the cloth object. The higher the value, the more stiff and less stretchable the cloth will be. Note that Iterations also has an effect and higher values will increase the Stiffness as well (which lets you simulate effects that resulted from setting the Stiffness to a value greater than 100% in previous versions).
这个参数控制布料物体的整体刚度。值越高,布料就越硬,弹性也就越差。注意,迭代也有效果,更高的值也会增加刚度(这使您可以模拟在以前的版本中将刚度设置为大于100% 的值所产生的效果)。
地图
The vertex map in this field controls the cloth’s stiffness value. The following can apply for any given point: The stiffness is set to 40% and the vertex map has a gradient of 100% to 0% applied to it. All points that receive a weighting of 100% have a stiffness of 40%. In turn, all points with a weighting of 50% will have a stiffness of 20%.
这个字段中的顶点映射控制织物的刚度值。下面的代码可以应用于任何给定的点: 刚度设置为40% ,顶点映射的梯度为100% 到0% 。所有接收到100% 权重的点具有40% 的刚度。反过来,所有加权50% 的点将有20% 的刚度。
屈曲[0. . 100% ]
As the name suggests, these springs make it possible for the cage to flex. Springs are created that connect an individual point of a given polygon with a point of another polygon, as long as these polygons are not adjoining. To put it differently: the spring omits one point between start and end points. The percentage value defines the strength with which the Cloth object will flex around the given points.
顾名思义,这些弹簧使笼子可以弯曲。创建弹簧是为了将给定多边形的单个点与另一个多边形的点连接起来,只要这些多边形不是相邻的。换句话说: 弹簧省略了起点和终点之间的一个点。百分比值定义了 Cloth 对象在给定点周围弯曲的强度。

地图
This vertex map defines where and how a cloth object’s springs work. If Flexion is set to 50%, all points with a weighting of 100% will have a Flexion of 50%; all points with a weighting of 50% will have a Flexion of 25%.
这个顶点映射定义了一个布料物体的弹簧在哪里以及如何工作。如果屈曲设置为50% ,所有点与100% 的权重将有一个50% 的屈曲; 所有点与权重的50% 将有一个25% 的屈曲。
橡胶[0. . 100% ]
This parameter controls the amount of stretching that the cloth object will be able to do. The default value of 0% will not allow for the cloth to stretch; whereas, a value of 100% will allow the cloth to be stretched. This parameter can also be controlled through a vertex map by using the respective field on the Effects tab.
这个参数控制布料对象能够进行的拉伸量。默认值0% 将不允许布料伸展; 而100% 的值将允许布料伸展。还可以通过使用 Effects 选项卡上的相应字段通过顶点映射控制此参数。

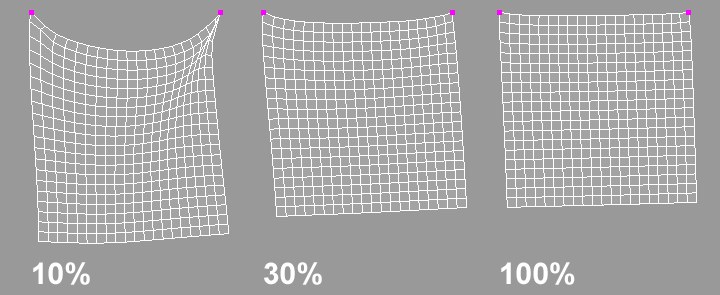
The image above shows three identical cloth objects with the exclusion that the Rubber setting has been altered. The higher that this value is, the more that the cloth objects can stretch.
上面的图片显示了三个相同的布料物体,排除了橡胶设置已经被改变。这个值越高,织物的拉伸能力就越强。
地图
A vertex map can also be applied, similar to the other spring types. This map controls where and how the cloth object should behave as rubber. If the rubber value is set to 50%, any point with a weighting of 100% will have a rubber value of 50%; any point with a weighting of 50% will have a rubber value of 25%.
也可以应用顶点映射,类似于其他弹簧类型。这张地图控制布料物体应该在哪里以及如何表现为橡胶。如果橡胶值设定为50% ,任何一个加权100% 的点将有50% 的橡胶值; 任何一个加权50% 的点将有25% 的橡胶值。
反弹[0. . + ∞% ]
This parameter controls the amount of bounce for the cloth object. This value is taken into account during a collision with a Collider object. The higher this value the more bounce will occur from the cloth object when colliding with an object. So, a very high value will cause the cloth to bounce away from the collision object. This value will also look at the Bounce value found in the Collider tag for the collision object.
这个参数控制布料物体的弹跳量。在与 Collider 对象发生碰撞时,会考虑这个值。这个值越高,当布料物体与物体碰撞时,反弹越多。因此,一个非常高的值会导致布料反弹离开碰撞物体。这个值还将查看碰撞对象的 Collider 标记中找到的 Bounce 值。
地图
Providing real world examples here will aid in understanding how this parameter affects cloth collisions. With a leather jacket, for example, this would create a high amount of bounce due to its sturdy, heavy surface. A woolen sweater, however, would create very little bounce because of its soft, airy surface.
在这里提供真实世界的例子将有助于理解这个参数如何影响布碰撞。例如,皮夹克,由于其坚固、沉重的表面,这会产生大量的反弹。然而,羊毛衫由于其柔软、通风的表面,弹性很小。
摩擦力[0. . 100% ]
Certain areas of a garment may have a lot of friction with its colliding surface, primarily in the collar and shoulder areas of a shirt, for example. But that’s not to say that one Friction value will be able to achieve this.
一件衣服的某些部位可能与其碰撞的表面产生很大的摩擦,主要是在衬衫的领子和肩膀部位。但这并不是说,一个摩擦值就能达到这个值。
地图
Painting these areas using a vertex map can specify what areas are stickier than others. A point weight value of 0% will have no friction, whereas a point weight value of 100% will have complete friction.
使用顶点映射绘制这些区域可以指定哪些区域比其他区域更具粘性。重量为0% 的点将没有摩擦,而重量为100% 的点将有完全的摩擦。
质量[0.1. . + ∞]
Different areas on a piece of fabric can have different mass values. Depending on if the garment has a pocket, a collar, a zipper, and so on those areas will carry more mass due to the extra amount of cloth involved.
织物上不同的区域有不同的质量值。这取决于衣服是否有口袋、领子、拉链等等,因为这些部位需要额外的布料。
地图
Specifying a vertex map in this field will allow for adding extra mass to those areas. With a Mass value of 2, a point that has been painted with 50% weight will now have a Mass value of 1.
在此字段中指定顶点映射将允许向这些区域添加额外的质量。当质量值为2时,一个重量为50% 的点现在质量值为1。
大小[1. . + ∞% ]
This will probably be most commonly used during the dressing state to fit the clothes to the character. Using a vertex map in this box will allow for certain areas on a garment to be shrunk or enlarged, tailoring the clothes to the character. As mentioned in the entry for the Size percentage setting at the top of the tab, a value of 100% is the original size of the object. With that, an area that has 50% weight painted in the vertex map will shrink to half the size of the original object.
这可能是最常用的在着装状态,以适应衣服的性格。在此框中使用顶点映射将允许衣服上的某些区域缩小或放大,并根据角色定制衣服。正如在选项卡顶部的 Size percentage 设置的条目中提到的,100% 的值是对象的原始大小。这样,在顶点映射中绘制了50% 权重的区域将缩小到原始对象的一半大小。
地图
A vertex map can only have a maximum value of 100%, so in order to enlarge an area the Size percentage value would need to be increased to a value greater than 100%. With a Size value of 200% an area with 50% weight will now be the original size of the object. An area with a weight value of 75% will now have a Size value of 150%.
一个顶点映射只能有100% 的最大值,所以为了扩大一个面积,大小百分比值需要增加到大于100% 的值。当 Size 值为200% 时,50% 重量的区域将成为对象的原始大小。重量值为75% 的区域现在的尺寸值为150% 。

In the image above different Vertex Maps where used to achieve different results when using Dress-O-matic. Note how the upper and lower t-shirt halves shrink depending on the weighting applied.
在上面的图像中,不同的顶点地图在使用 Dress-O-matic 时取得不同的结果。注意上半身和下半身的 t 恤衫是如何收缩的,这取决于所用的重量。
撕裂[1. . + ∞% ]/使用撕裂

地图
With this option enabled the cloth engine will allow for tearing to take place during the simulation. But in order for this tearing to work, the Cloth object to which the tag is assigned must be a Child of the Cloth Surface object. In other words, the Cloth object is the actual surface that will be torn, not the original cloth object. A tear is determined by the Stiffness of the cloth object. The lower the amount of Stiffness the easier it is for the cloth to be torn, with the exception that a maximum limit must be defined at which the tear will occur.
有了这个选项启用的布料引擎将允许撕裂发生在模拟。但是为了使这种撕裂工作,布对象的标签分配必须是一个子的布表面对象。换句话说,布对象是实际的表面将被撕裂,而不是原来的布对象。撕裂取决于布料物体的硬度。硬度越低,织物就越容易被撕裂,但是必须规定撕裂的最大限度。
Tearing can also be controlled even further with vertex maps. As stated previously, tearing is based on the stiffness of the cloth; so using a vertex map in the Stiffness setting on the Effects tab will give you ultimate control over cloth tears.
撕裂也可以通过顶点映射进一步控制。如前所述,撕裂是基于布料的刚度,所以使用顶点贴图的刚度设置的效果标签,将给你最终控制布料撕裂。
