Caustics
焦散
Basic 基础
Caustics
焦散
With Advanced Render’s powerful caustics engine, you can create realistic patterns of focused light such as the
bright patches that a whiskey tumbler casts onto a wooden floor. For a general introduction to caustics,
including commonly-used terms, look up What are caustics? in the index.
使用高级渲染的强大焦散引擎,你可以创建聚焦光线的现实模式,如明亮的补丁,威士忌酒杯投放到木地板上。对于焦散线的一般介绍,包括常用的术语,查找什么是焦散线?在索引中。
You use three dialogs to set up caustics. On the Caustics page of the render settings, set the basic properties
of the caustics effect such as its strength. On the Caustics page of each light source (Attribute Manager), refine the effect for light sources. On the Illumination page of
the Material Editor, fine-tune the caustics effect for any material. Note that you can also access the
caustics settings for materials via the Attribute Manager, provided that you have
selected the desired material.
你使用三个对话框来建立焦散线。在渲染设置的焦散页面上,设置焦散效果的基本属性,比如它的强度。在焦散页的每个光源(属性管理器) ,细化效果的光源。在材质编辑器的照明页面上,微调任何材质的焦散效果。注意,你也可以通过属性管理器访问材质的焦散设置,只要你已经选择了所需的材质。
Parameters
参数
-
Use the options on the Photon Caustics page to define basic properties of the effect.
使用光子焦散页面上的选项来定义效果的基本属性

-
You can refine the caustics effect for each material using the caustics settings on the Illumination page of
the Material Editor or 你可以使用材质编辑器的照明页面上的焦散设置来精炼每种材质的焦散效果Attribute Manager 属性管理器.

Enable this option if you want the material to generate Photon caustics. Enter the strength of the effect into
the input box.
如果你想要材质产生光子焦散,启用这个选项。在输入框中输入效果的强度
The material must be transparent and/or reflective in order to create a caustics effect.
材质必须透明和/或反射,以创建焦散效果
-
You can switch on caustics for any light source and refine the effect using the light’s Caustics page in the
你可以打开任何光源的焦散,并使用光的焦散页在Attribute Manager 属性管理器.

Tip:
提示:
There are 2 types of caustics in Cinema 4D: 在C4D 中有两种焦散线:- The photon caustics (these are described in this
section): Faster than GI Caustics but must be generated using individual light sources. They can be rendered
volumetrically. 光子焦散线(这些描述在这一节) : 比 GI 焦散线快,但必须使用单个光源产生。它们可以被体育地渲染
- GI-Caustics Gi- 焦散线: Not very precise
caustics in conjunction with IR modes (a quick but effective trick: assign a Compositing tag with activated
: 不是非常精确的焦散结合红外模式(一个快速但有效的伎俩: 分配与激活合成标签Enable Forced QMC Sampling 启用强制 QMC 抽样) but
they do react to all illuminated surfaces within the scene. )但它们确实会对场景中所有被照亮的表面产生反应
Both caustics types are completely
indpendent of one another and are rendered using completely different methods. However, they can be used
either separately or combined. 这两种焦散类型是完全独立的另一个和呈现使用完全不同的方法。但是,它们既可以单独使用,也可以组合使用
What are caustics?
什么是焦散?
Caustics are patterns of focused light created by curved surfaces that are reflective or refractive.
焦散线是由具有反射性或折射性的弯曲表面产生的聚焦光线图案。
Advanced Render enables you to create both surface caustics and volume caustics.
高级渲染可以创建表面焦散和体焦散。
 Copyright by Janine Pauke . Figure 1: The
transparent sphere focuses light onto the tile to create a caustics effect (in this case, a bright
spot). 版权所有: Janine Pauke。图1: 透明球体将光线聚焦到瓷砖上,创建焦散效果(在这个例子中,是一个亮点)
Copyright by Janine Pauke . Figure 1: The
transparent sphere focuses light onto the tile to create a caustics effect (in this case, a bright
spot). 版权所有: Janine Pauke。图1: 透明球体将光线聚焦到瓷砖上,创建焦散效果(在这个例子中,是一个亮点)
- A surface caustics effect shows up on object surfaces only — examples are the transparent sphere and the
ring (in both cases, the effect shows up on a surface: the floor). 表面焦散效果只表现在物体表面上ーー例如透明球体和圆环(在这两种情况下,效果都表现在一个表面上: 地板)
 Figure 2: The metal ring shows a caustics effect
generated by a reflective surface. 图2: 金属环显示了由反射表面产生的焦散效果
Figure 2: The metal ring shows a caustics effect
generated by a reflective surface. 图2: 金属环显示了由反射表面产生的焦散效果
- Volume caustics are visible as they pass through 3D space — they do not need a surface to
illuminate. 体焦散线是可见的,因为他们通过三维空间-他们不需要一个表面照明
See Figure 3. 见图3
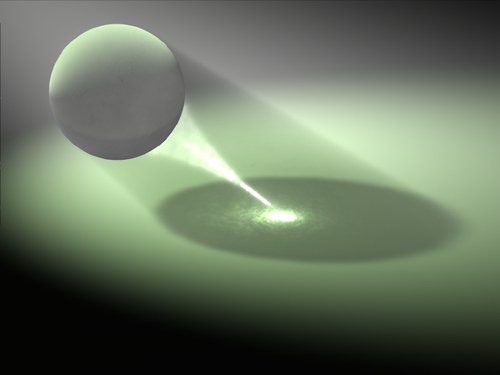 Figure 3: The bright 图3: 光明tail 尾巴 extending from the sphere is a volume caustics effect. 从球体延伸出来的是体积焦散效果
Figure 3: The bright 图3: 光明tail 尾巴 extending from the sphere is a volume caustics effect. 从球体延伸出来的是体积焦散效果
The surface caustics algorithm
表面焦散线算法
For surface caustics, you need:
对于表面焦散,你需要:
- A light source that emits photons — enable surface caustics (in the 发射光子的光源ーー能够实现表面焦散Attribute
Manager 属性管理器, on the light’s Caustics page); ,在光线的焦散页) ;
- An object with a material that generates surface
caustics — the material must be transparent or reflective or both. The object must be curved in a way that
focuses light; 使用能产生表面焦散的材质的物体ーー材质必须是透明的或反光的,或者两者兼而有之。物体必须是弯曲的,以便聚焦光线;
- An object to receive the surface caustics. 接收表面焦散线的物体
Caustics are calculated in a very different way to global illumination and raytracing. Global illumination and
raytracing send rays from the camera into the scene. With caustics, however, photons are sent from the light
source into the scene. Each photon is given a starting energy. A photon’s energy is reduced as it passes
through the scene and is reflected or refracted by object surfaces (Figure 4).
焦散线的计算方法与全局光源和光线追踪完全不同。全局光源和光线追踪将光线从相机发送到场景中。然而,在焦散线中,光子从光源发射到场景中。每个光子都有一个起始能量。当光子穿过场景时,它的能量减少,并且被物体表面反射或折射(图4)。
 Figure 4: A photon refracted by a
sphere. 图4: 一个光子被一个球体折射
Figure 4: A photon refracted by a
sphere. 图4: 一个光子被一个球体折射
When a photon hits a reflective or transparent surface, the photon is reflected or refracted. The photon loses
some energy in the process and the material’s properties are taken into account.
当一个光子撞击一个反射或透明的表面时,光子被反射或折射。光子在这个过程中损失了一些能量,同时考虑了材质的性质。
For example, if the surface reflects or refracts blue light only, the photon’s color changes to blue. If the
photon still has some energy left at this point, it continues to fly through the scene. When the photon hits a
surface that is neither reflective nor transparent, the photon ends its journey there and its values are
stored in a data structure called the photon tree — later, the values in the photon tree will be interpolated
to calculate the caustics effect.
例如,如果表面只反射或折射蓝光,光子的颜色就会变成蓝色。如果光子在这一点上仍然有一些能量,它就会继续穿过这个场景。当光子撞击到一个既不反射也不透明的表面时,光子在那里结束了它的旅程,它的值被存储在一个称为光子树的数据结构中ーー稍后,光子树中的值将被插值以计算焦散效果。
You can prevent a material from receiving the surface caustics
effect. Photons that hit such surfaces will end their journey there and their values will not be saved in the
photon tree — this prevents the material from receiving a caustics effect. 你可以阻止材质接收表面焦散效果。撞击这些表面的光子将在那里结束它们的旅程,它们的价值将不会被保存在光子树中ーー这就阻止了材质接收焦散效果
Once all photons have ended their journey in one way or another, the values in the photon tree are interpolated
to calculate the surface caustics effect for the image.
一旦所有的光子以这样或那样的方式结束了它们的旅程,光子树中的值被插值以计算图像的表面焦散效果。
Double-caustics are possible. This happens when an object focuses caustics onto another object that generates
caustics. See Figure 5.
双焦散是可能的。当一个物体聚焦焦散到另一个产生焦散的物体上时,就会发生这种情况。见图5。
 Figure 5: An example of
double-caustics. 图5: 双焦散线的一个例子
Figure 5: An example of
double-caustics. 图5: 双焦散线的一个例子
The volume caustics algorithm
体积焦散线算法
Volume Photon caustics are calculated in a similar way to surface caustics. First you need the following:
体积光子焦散线的计算方法与表面焦散线的计算方法相似:
- A volumetric light source to send out photons — enable volume caustics ( 用于发射光子的体积光源ーー使体积焦散线(Attribute
Manager 属性管理器, Caustics page of the light source); ,焦散页的光源) ;
- An object with a material that generates volume
caustics — the material must be transparent or reflective or both. The object must be curved in a way that
focuses light. 使用能产生体积焦散线的材质的物体ーー材质必须是透明的或反射的,或者两者兼而有之。物体必须是弯曲的,以便聚焦光线
As with surface caustics, when a photon hits a reflective or transparent surface, the photon is reflected or
refracted. The photon loses some energy in the process and the material’s properties are taken into account.
For example, if the surface reflects or refracts green light only, the photon’s color changes to green.
Provided the photon still has energy, it then continues to fly through the scene.
和表面焦散一样,当一个光子撞击一个反射或透明的表面时,光子会被反射或折射。光子在这个过程中损失了一些能量,同时考虑了材质的性质。例如,如果表面只反射或折射绿光,光子的颜色就会变成绿色。如果光子仍然有能量,那么它就会继续在场景中飞行。
In contrast to surface caustics, the photons of volume caustics are saved in the photon tree at regular
intervals. When the photon hits a surface that is neither reflective nor transparent, the photon ends its
journey there. Once all photons have completed their journey, the values in the photon tree are interpolated
to calculate the volume caustics effect for the image.
与表面焦散相比,体焦散的光子以规则的间隔保存在光子树中。当光子撞击到一个既不反射也不透明的表面时,光子的旅程就到此结束。一旦所有的光子完成了它们的旅程,光子树中的值被插值以计算图像的体积焦散效果。
Troubleshooting Surface Caustics
表面焦散故障排除
The best Photon caustics settings depend on factors specific to the scene such as the distance between the
light source and the object that is generating caustics. However, the following steps should help you to
achieve a good result.
光子焦散线的最佳设置取决于场景特定的因素,如光源和产生焦散线的物体之间的距离。然而,下面的步骤应该可以帮助你达到一个好的结果。
- On the light’s Caustics page ( 在光的焦散页(Attribute Manager 属性管理器), set Energy to a high value
(e.g., 100,000%) and Photons to a low value (e.g., 100). This will enable you to see the individual photons as
points of light so that you can check if enough photons (if any at all) are reaching the important area. If
you can’t see any photons, check the following: ) ,将能量设定为高值(例如100,000%) ,光子设定为低值(例如100)。这将使你能够看到单个的光子作为光点,这样你就可以检查是否有足够的光子(如果有的话)到达重要的区域。如果你看不到任何光子,请查看以下内容:
- Is the light pointing in the right
direction? 光线指向正确的方向吗?
- Are the caustics options enabled in the following places?: render settings (Caustics page),
light settings ( 在下列地方是否启用焦散选项?: 渲染设置(焦散页) ,灯光设置(Attribute Manager 属性管理器 / Caustics page) and Material Editor
(Illumination page). /焦散页)和材质编辑器(照明页)
- Does the object that should generate caustics have a reflective and/or
transparent material? 产生焦散线的物体是否有反射和/或透明材质?
- Once you can see the photons, increase the Photons value (and perhaps the
Energy) until you achieve a good caustics effect. To fine-tune the sharpness, adjust Radius and Samples on the
Illumination tab (Material Editor). 一旦你可以看到光子,增加光子值(或许还有能量) ,直到你达到一个好的焦散效果。调整锐度,调整半径和样品的照明标签(材质编辑器)
Troubleshooting Volume Caustics
解决体积焦散问题
If you notice artifacts of the type illustrated below when rendering volume caustics, on the light’s Visibility
tab, try reducing the Sample Distance value. This will, however, add to the render time.
如果你在渲染体焦散线的时候注意到下面说明的工件,在灯光的可见性标签上,尝试减少样本距离值。然而,这会增加渲染时间。
 Reduce the Sample Distance to remove the artifacts
indicated above. For this example, Sample Distance was set to 25 (left) and 5 (right). 减少采样距离以移除上面提到的工件。对于本例,Sample Distance 被设置为25(左)和5(右)
Reduce the Sample Distance to remove the artifacts
indicated above. For this example, Sample Distance was set to 25 (left) and 5 (right). 减少采样距离以移除上面提到的工件。对于本例,Sample Distance 被设置为25(左)和5(右)








